REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS
-
Plants reproduce through asexual and sexual methods of reproduction.
-
Asexual reproduction involves the simple division of the plant body into two or more parts or spore formation.
-
New plant body is formed from a single parent. This happens under favourable conditions.
-
Sexual reproduction takes place by the formation of seeds.
-
It involves two parents and the fusion of male and female reproductive cells called gametes to form a single cell called the zygote.
Asexual Reproduction:
-
Asexual reproduction is the simplest form of reproduction found in plants. It is of three common forms:
Budding
Fragmentation
Spore formation
Budding:
-
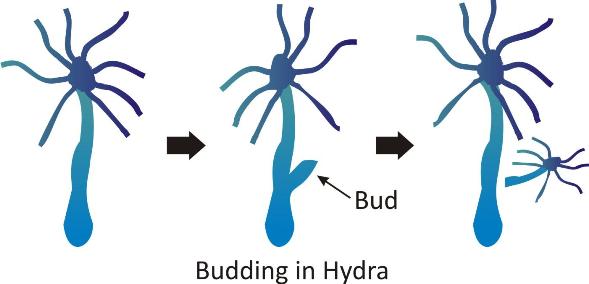
Microscopic organisms, such as yeast and Hydra, reproduce asexually by budding.
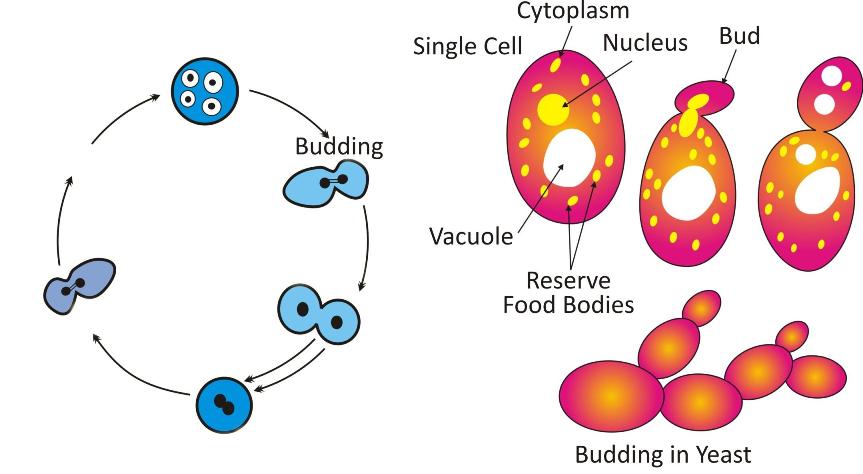
Budding in yeast
-
In this process, a small bulb-like cellular outgrowth is formed from the cell called a bud.
-
This bud keeps on increasing in size and forms an independent organism which separates from the parent.
Fragmentation:
-
It is a very common form of asexual reproduction in the plant kingdom, e.g., algae.
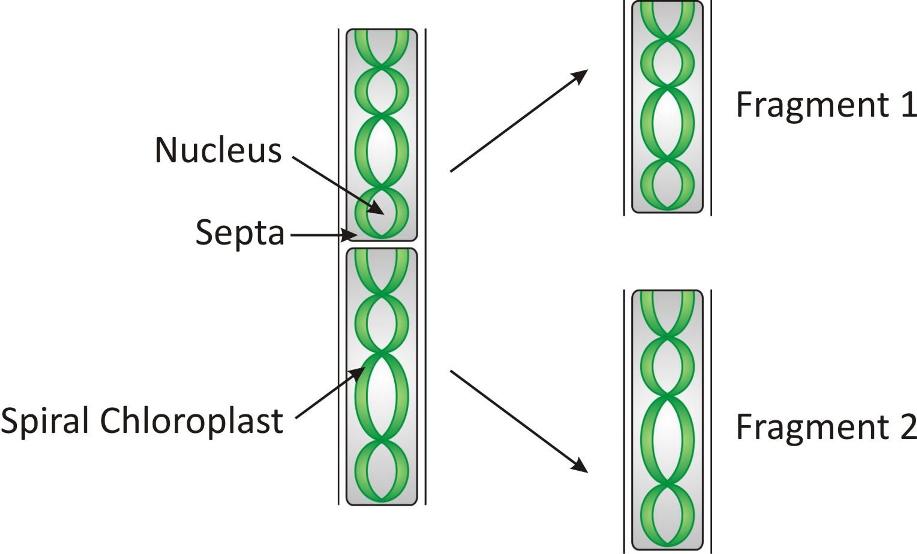
Fragmentation in spirogyra
-
Algae, such as Spirogyra (pond silk), Fucus, etc., are the slimy, green, and small plants seen floating on the surface of ponds or in dirty drains.
-
In this process, the adult organism just breaks up into two or more pieces called fragments.
-
Each of these fragments grows up to become a new plant.
Spore Formation:
-
Some plants such as ferns and mosses multiply asexually through spores.
-
Spores are microscopic single-celled or several-celled reproductive bodies that are mostly spherical in shape.
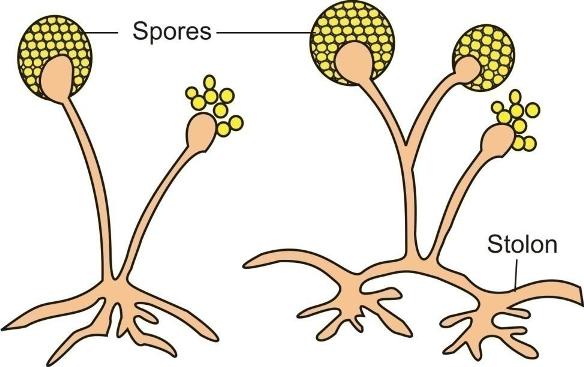
Spore formation
-
They are protected by a thick wall when conditions (such as humidity and temperature) are unfavourable.
-
Once the conditions for germination are favourable, these spores burst out of the thick wall, start multiplying, and grow into new plants.
Vegetative Reproduction:
-
Vegetative reproduction is also a type of asexual reproduction in which a cell, tissue, or part of an organ of a plant develops into a new organism.
-
In some plants, vegetative parts such as root, stem, and leaf can be used to produce new plants.
-
This can be done by natural as well as artificial methods.



