PETROLEUM AND NATURAL GAS
-
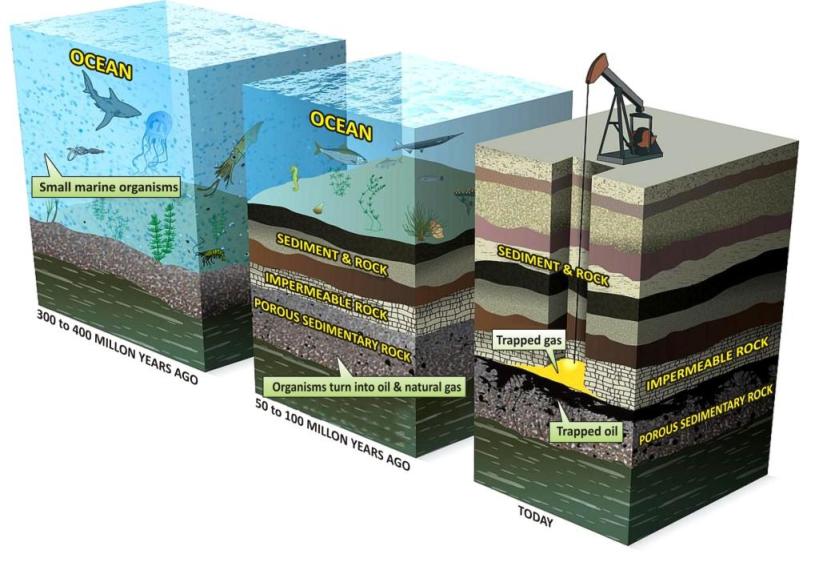
Petroleum and natural gas were formed from the remains of tiny marine organisms that died millions of years ago.
Formation of Petroleum and natural gas:
-
As small organisms called plankton die they sink to the bottom of the sea.
-
Over time, this layer of dead organisms was covered beneath sediments.
-
Enormous heat and pressure transformed these remains to petroleum and natural gas.
-
Rising through porous rocks such as sandstone, petroleum and natural gas reached a layer of impermeable rock and were trapped below it.
Extraction of Petroleum:
-
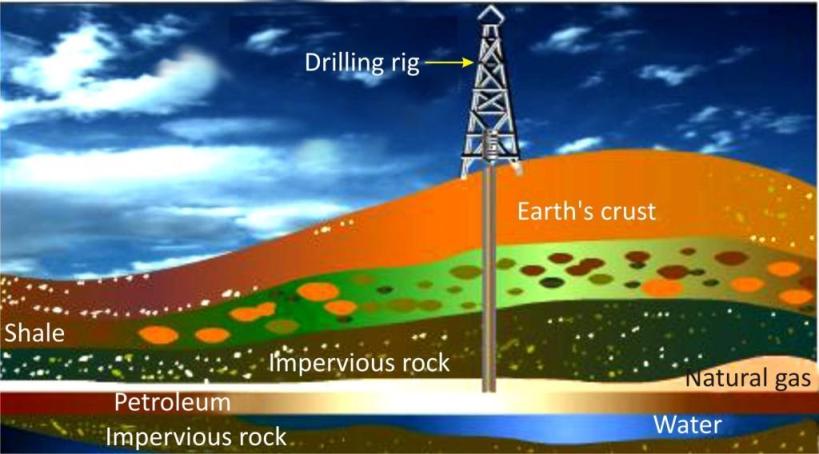
Petroleum reserves exist as oil or gas within trapping sections of reservoir rock formed by structural and or stratigraphic geologic features.
-
Water is the predominant fluid found in the permeability and porosity of subsurface strata within the earth's crust.
-
Both oil and gas have a low specific gravity relative to water and will thus, float through the more porous sections of reservoir rock from their source area to the surface unless restrained by a trap. Typically, reservoir rock consists of sand, sandstone, limestone, or dolomite.
-
A trap is a reservoir that is overlain by a dense cap rock or a zone of very low or no porosity that restrains migrating hydrocarbon.
-
Petroleum bearing reservoirs can exist from surface seeps to subsurface depths over 4 mi (6.4 km) below sea level.
-
Reservoirs vary from being quite small to covering several thousands of acres, and range in thickness from a few inches to hundreds of feet or more.
-
Petroleum and natural gas are extracted by drilling through the impermeable rock.
Refining of Petroleum:
-
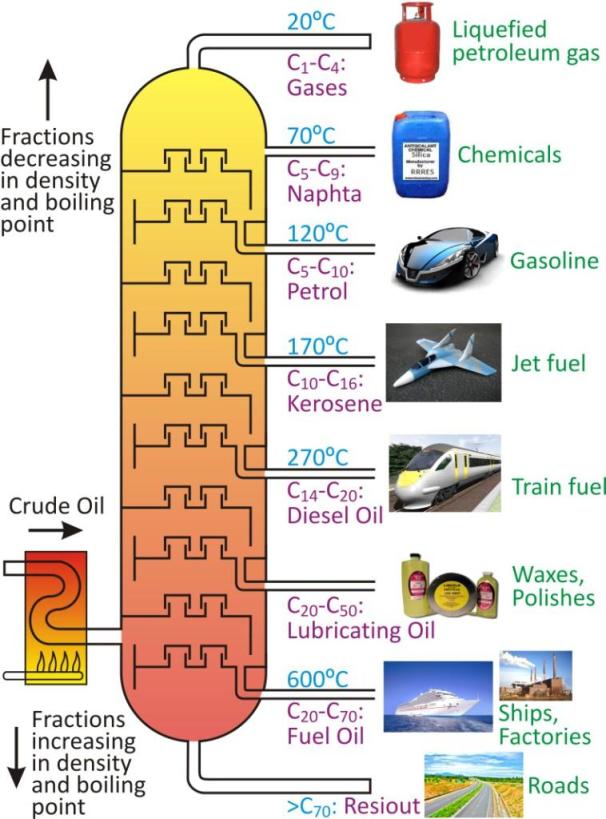
Crude oil is a complex mixture of solid, liquid and gaseous hydrocarbons. It is separated into useful substances through a process called refining of petroleum.
-
Petroleum or crude oil is a complex mixture of solid, liquid, and gaseous hydrocarbons.
-
Refining of petroleum is done for separation of useful substances in oil refineries. Refining of petroleum is done by fractional distillation.
-
In this process, petroleum is heated to 400°C and introduced in a fractionating column, which is a tall, cylindrical structure fitted with horizontal trays.
-
As the vapours of petroleum rise inside the fractionating column, they cool and condense at different heights, depending on their boiling points, and are collected in different trays. Uncondensed hydrocarbons (petroleum gas) pass out of the column.
Natural gas:
-
Natural gas consists mainly of methane. It has the following main uses.
-
It is used for the generation of electricity.
-
Compressed natural gas (CNG) is used as a fuel in automobiles as it is more environment-friendly than petrol or diesel. It is also used as a domestic fuel.
-
It is used in the production of ammonia.
-
It is used to produce hydrogen.
-
It is used in the manufacture of steel, glass, plastics, and other products.
Limitations of Fossil Fuels:
-
The two main limitations of fossil fuels are their limited availability in nature and the air pollution caused due to their use.
Limited availability:
-
Fossil fuels take millions of years to form. If we run out of the existing stock of these fuels, we will not get more until natural processes have regenerated them.
Air pollution:
-
The addition of undesirable substances to the air is called air pollution. These undesirable substances, which can adversely affect organisms, are called pollutants. Pollutants can be in the form of particles or gases.


