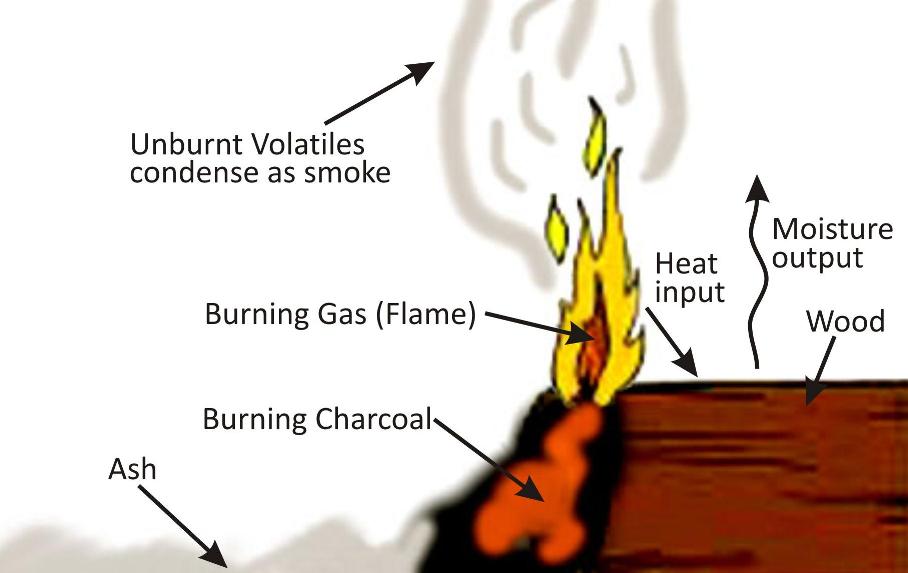
COMPLETE AND INCOMPLETE COMBUSTION
-
Complete combustion needs a plentiful supply of air so that the elements in the fuel react fully with oxygen.
-
Fuels such as natural gas and petrol contain hydrocarbons. These are compounds of hydrogen and carbon only. When they burn completely:
-
Carbon oxidises to carbon dioxide
-
Hydrogen oxidises to water - Water, H2O, is an oxide of hydrogen
General reaction for complete combustion:
-
Hydrogen + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water
-
Incomplete combustion occurs when the supply of air or oxygen is poor.
-
Water is still produced, but carbon monoxide and carbon are produced instead of carbon dioxide.
General reaction for incomplete combustion:
-
Hydrogen + Oxygen → Carbon monoxide + Carbon + Water
-
Carbon is released as soot. Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas, which is one reason why complete combustion is preferred to incomplete combustion.
-
Gas fires and boilers must be serviced regularly to ensure they do not produce carbon monoxide.