AUTOTROPHIC NUTRITION
-
Organisms which utilise carbon dioxide as their sole source of carbon for the formation of organic food by the process of photosynthesis are called autotrophs (self nourishing).
-
The type of nutrition carried out by autotrophs is termed as autotrophic nutrition.
-
In this type of nutrition, the living organisms manufacture their own organic food from simple inorganic raw materials.
-
The green plants exhibit autotrophic mode of nutrition and hence are called the autotrophs.
-
The autotrophs require external energy source for the manufacture of organic substances.
-
Green plants obtain energy from sunlight and therefore are called photoautotrophs.
-
The process of synthesizing food in plant is called photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis:
-
This term was coined by Charles Reid Barnes in 1883.
-
Plants are producers, and producers make their own food.
-
This food is in the form of a sugar (often glucose).
-
Sugars are made during a process called photosynthesis from carbon dioxide and water.
-
The end products, organic compounds, are made from the simple inorganic compounds- water and carbon dioxide.
-
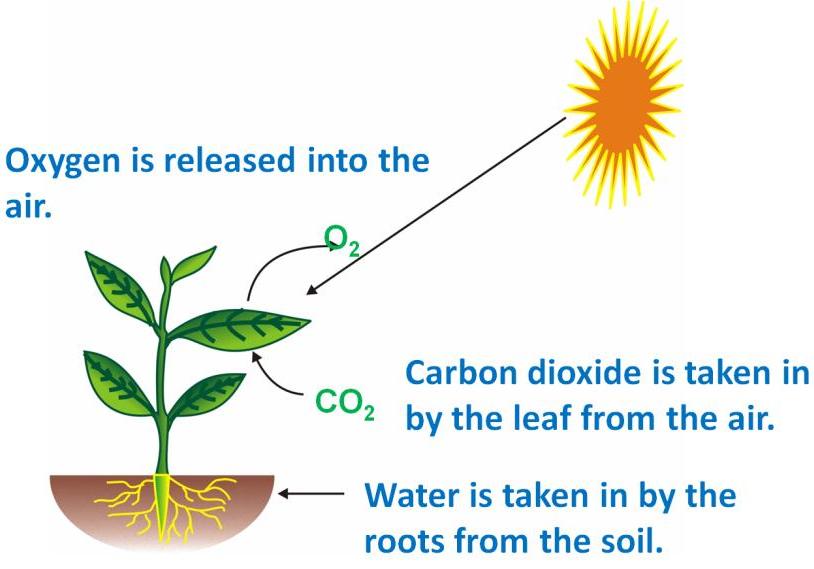
The two raw materials required for photosynthesis are acquired by different means.
-
Carbon dioxide is absorbed by the leaves while water is obtained by the roots from the soil.
-
In order for the reaction to take place, energy comes from light (usually the sun) and is stored within the sugar which is an energy-rich molecule.
-
The reaction that takes place can be written as:

-
The process of using the energy of sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates (starch) and oxygen is called photosynthesis.
Conditions Necessary for Photosynthesis:
-
The general conditions necessary for photosynthesis are:
-
The presence of a green pigment called chlorophyll.
-
The availability of carbon dioxide.
-
Availability of water.
-
The presence of sunlight.

