GREENHOUSE EFFECT AND GLOBAL WARMING
Greenhouse effect:
-
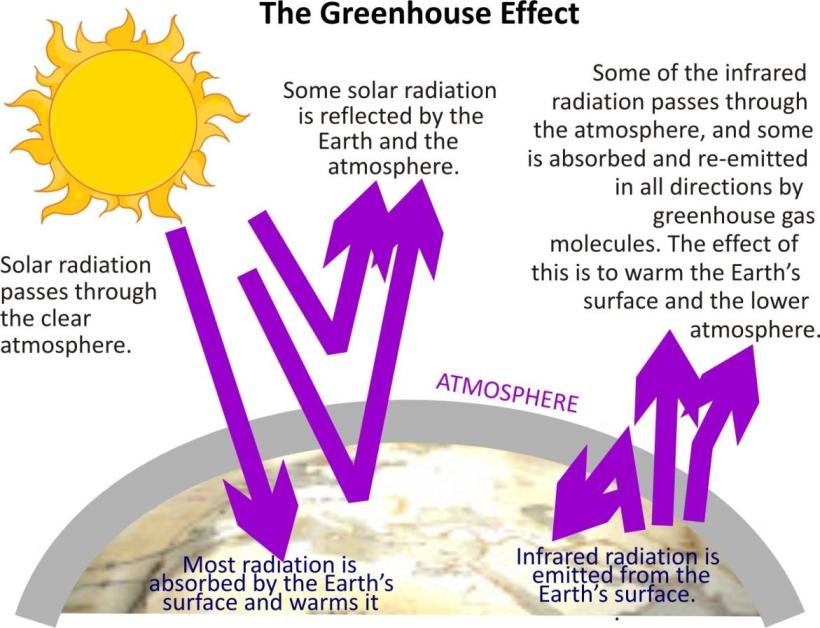
The phenomenon whereby the earth's atmosphere traps solar radiation, due to the presence of various atmospheric gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, and methane that allow incoming sunlight to pass through but absorb heat radiated back from the earth's surface.
-
Incoming solar radiations have shorter wavelength thus more penetrating power so they can reach the surface easily but the outgoing infrared radiations with higher wavelength possess less penetrating power. Hence outgoing radiations cannot escape the atmosphere and get trapped by the atmospheric gases. This increases the atmospheric temperature.
-
The natural greenhouse effect is important so as to maintain the temperature of earth’s surface to support the life.
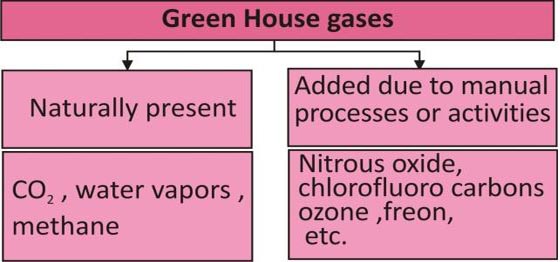
Green house gases:
-
Accumulation of gases in the environment tends to increase the greenhouse effect which leads to the global warming.
-
Global warming is defined as the tremendous increase in the temperature of earth’s atmosphere due to change in the normal concentration of gases.

-
Global warming has drastic effects on biotic and abiotic components.

-
Overall increase in temperature.
-
Melting of the polar ice caps.
-
Rise in the level of ocean waters.
-
Change in the rainfall pattern.
-
Affects the biodiversity
-
Affects the agricultural practices.
-
Affects the survival of plants and animals.
-
Ozone layer depletion etc.
Ozone layer depletion:
-
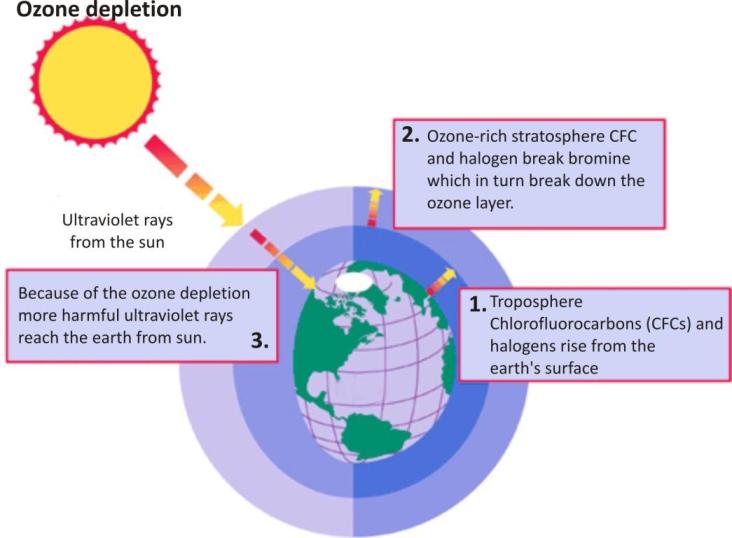
Accumulation of chlorofluorocarbons in the atmosphere breaks ozone molecules and thus depletes the ozone layer.
-
CFCs are used in some spray cans to force the contents out of the can.
-
They are also used in refrigerators, air conditioning systems and some fire extinguishers.
-
They are used because they are not poisonous and do not catch fire.
-
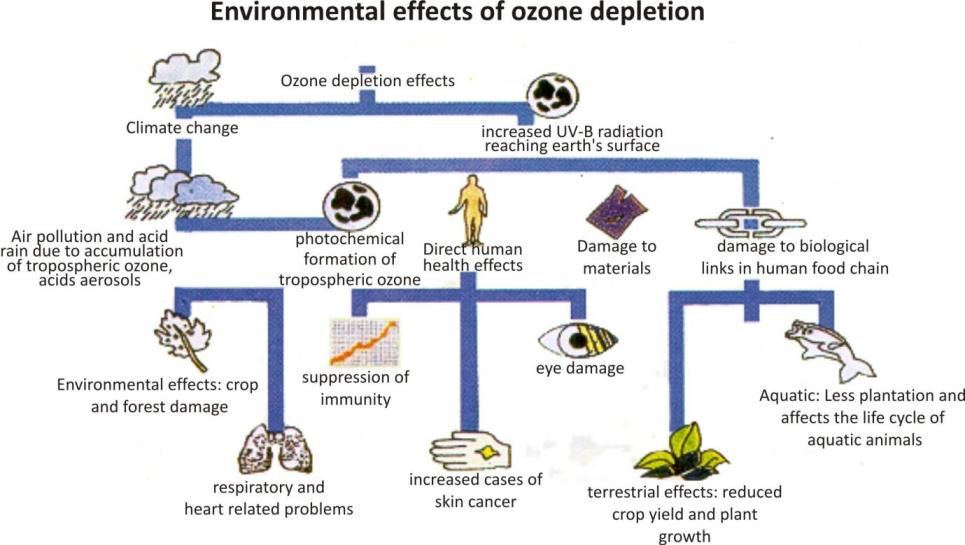
This depletion can affect the human health, aquatic life, plants animals and materials.
Biological problems:
-
Photochemical smog, acid rain and global warming can affect different organisms in different ways.
Effect on humans:
-
Inhalation of polluted air causes many different types of diseases in human beings.
-
Human beings suffer from diseases of trachea and lungs.
-
Diseases like cancer of lungs, damage to kidney and night blindness are caused.
-
Blood pressure increases/decreases.
-
The reproduction power of men decreases.
-
Life span decreases.
Effect on animals:
-
Milk producing capacity of milk animals decreases.
-
Their life span decreases.
-
They develop physical defects.
-
Skin becomes rough.
Effect on plants:
-
Leaves of plants fall down. So the process of photosynthesis becomes slow.
-
New shoots of plants are destroyed.
-
Growth of a plant is stunted.
-
Flowers and fruits fall down.
Case study: Bhopal gas tragedy:
-
Bhopal gas tragedy occurred on 3rd December 1984 in Bhopal. A poisonous gas methyl isocyanate was leaked from a pesticide industry and caused a disaster in the city, the effects of which are still persisting. This tragedy killed thousands of people and millions of people exposed were injured and suffered from multiple ailments like:
-
Eye diseases: Cataract, conjunctivitis, poor vision, complete blindness etc.
-
Neurological problems: reduction in memory skills and motor skills.
-
Lung diseases: Bronchitis, Breathlessness, cough etc.
-
High body temperature and low immunity.
-
Skeletal and muscular problems.
-
It caused a panic for those also which were still not born as it resulted in congenital diseases in them. Tons of toxic material was disposed which seeped into groundwater and causing water pollution.

Prevention of Air pollution:
-
Natural causes of air pollution are not under our control but some measures can be taken to control manual activities.
-
Measures must be taken to decrease the amount of particles and toxic gases at the site of its production.
-
If pollution is caused by some raw material, another raw material should be used which spreads less pollution.
Example: use of unleaded petrol.
-
Industrial area should be kept away from human residence.
-
Waste eliminated from industries should be treated/ detoxified before its elimination in the air.
-
Vehicles or other machineries should be checked at regular intervals.
-
Carbon particles in smoke should be controlled using proper fuel. Antismoke law should be strictly implemented.
-
Instead of petrol and diesel, other fuels like CNG should be used for our vehicle.
-
Alternative energy resources of energy should be used. (E.g. Solar energy, Hydro energy)
-
More trees should be planted and carefully grown. Plants have great contribution in controlling balance of gases in atmosphere.
-
Destruction of forests should be stopped and more forests should be developed.






