PROPERTIES OF DIFFERENT STATES OF MATTER
Solid state:
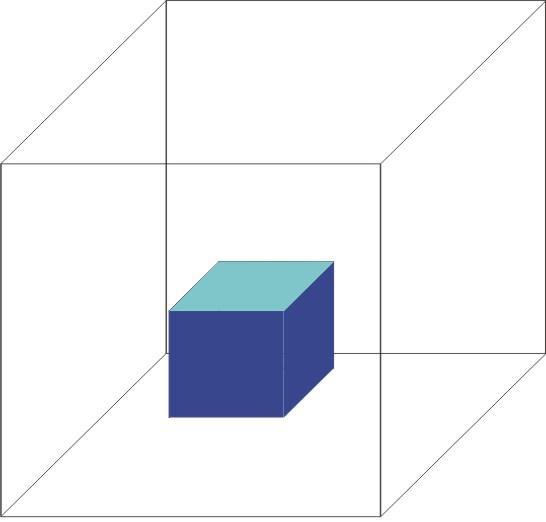
Solid
Fixed shape
Fixed volume
Solids are rigid, and have negligible compressibility:
Reason:
-
Molecules are closely spaced and the intermolecular separation is very small which cannot be reduced further.
Example:
-
Shape of elastic solids like rubber can be changed by applying force on it but it regains its shape once the force is removed.
-
It is not possible to change the shape of a rock by applying force it will break into pieces.
-
Sponge can be compressed because of its porous nature but it also regains its shape once the force is removed.
-
Solids have fixed shape and definite volume.
Reason:
-
The intermolecular force of attraction is very strong. The molecules are strongly held and arranged in order.
-
Solids break but it is difficult to change their shape.
-
A solid does not diffuse into another solid easily.
Reason:
-
Intermolecular force of attraction is very strong.
-
A solid does not flow and can be stored in a container.
Reason:
-
Intermolecular force of attraction is so strong that molecules do not flow and leave the surface of the solid.
-
Solids have their melting and boiling points above room temperature.
For example:
-
Melting point of iron is 1,535º C, melting point of copper is 1,085º C
Liquid state:
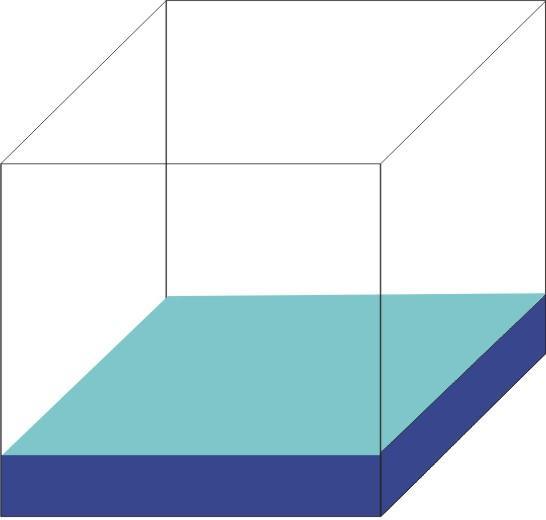
Liquid
Shape of container
Free surface
Fixed volume
-
Liquids have fixed volume but no fixed shape.
Reason:
-
The intermolecular force of attraction is weak. The molecules are are not arranged in order.
-
Liquids are not rigid and can be compressed to some extent.
Reason:
-
The intermolecular separation is more as compared to solids which can be reduced further.
-
Liquids flow from higher to lower level.
Reason:
-
Intermolecular force of attraction is weaker than that present in solids so the molecules can flow.
-
Liquids have their boiling points above room temperature, under normal conditions.
-
Solids, liquids and gases can diffuse into liquids. The rate of diffusion of liquids is higher than that of solids. This is due to the fact that in the liquid state, particles move freely and have greater space between them as compared to particles in the solid state.
Gases:
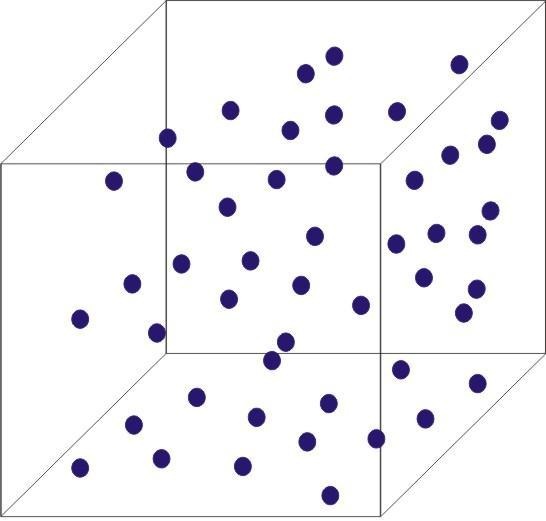
Gas
Shape of container
Volume of container
-
All the gases show following characteristics:
-
Gases are highly compressible, i.e. gases can be compressed easily by applying pressure.
Reason:
-
Molecules are far of from each other and the intermolecular separation is very large.
-
The liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) cylinder that we get in our home for cooking or the oxygen supplied to hospitals in cylinders is compressed gas. Compressed natural gas (CNG) is used as fuel these days in vehicles. Due to its high compressibility, large volumes of a gas can be compressed into a small cylinder and transported easily.
-
Gases do not have fixed volume and shape. Gases fill the container of any size and shape completely.
-
Gases can diffuse into each other rapidly.
-
Gases have their melting and boiling points both below room temperature.
Pressure exerted by gas:
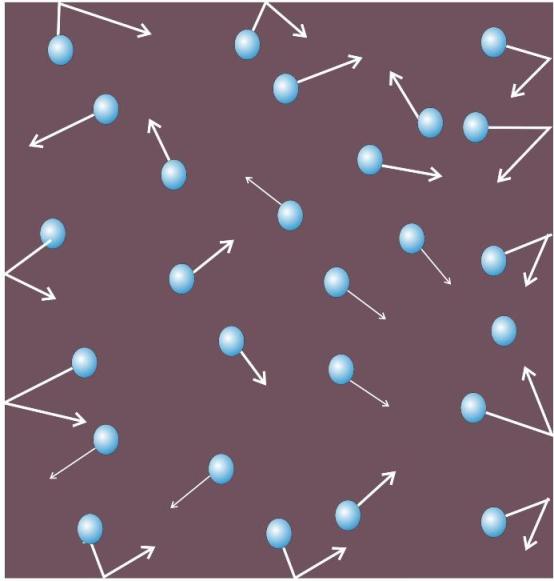
Gas Molecules collide with each other and with the wall of vessel
-
The particles of gas move about randomly at high speed.
-
Due to this random movement, the particles hit each other and also the walls of the container.
-
The pressure exerted by the gas is because of this force exerted by gas particles per unit area on the walls of the container.



