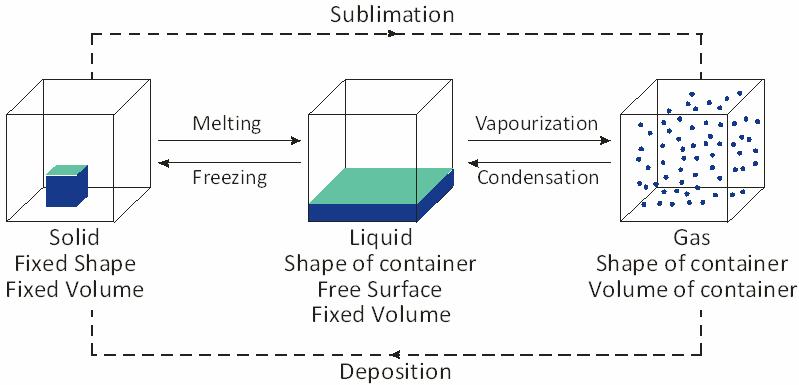
CHANGE IN STATE OF MATTER
Matter can be change from one state to another by:
-
Changing the temperature
-
Changing the pressure
Effect of Change of Temperature:
-
On increasing the temperature, a solid can be converted into liquid state; and a liquid can be converted into gaseous state.
-
On decreasing the temperature, a gas can be converted into liquid state. And a liquid can be converted into solid state.
Melting:
-
The process, in which a solid substance changes into its liquid state on heating, is called melting (or fusion).
-
The temperature, at which a solid substance melts and changes into liquid at atmospheric pressure, is called melting point of the substance.
-
Different solids have different melting points.
-
The melting point of ice is 0ºC; the point of wax is 63ºC, iron is 1535ºC.
-
When a solid substance is heated, the heat energy supplied gets stored as potential energy of particles.
-
The potential energy increases which results in the increase in the intermolecular distance and decrease in the intermolecular force of attraction between the particles thus the molecules become comparatively free.
-
When more heat is supplied the molecules vibrate vigorously thus changing the state.
Melting point:
-
The temperature at which a solid melts to become a liquid at the atmospheric pressure is called its melting point.
-
The melting point of ice is 273.16 K*. The process of melting, that is, change of solid state into liquid state is also known as fusion.
Latent Heat of Fusion:
-
When a solid substance is heated it melts and changes into liquid state at its melting point. The temperature will remain constant at the melting point until the entire solid has melted.
-
The amount of heat needed to melt the solid depends only on the mass of the solid.
-
As this heat energy is absorbed by ice without showing any rise in temperature, it is considered that it gets hidden into the contents of the beaker and is known as the latent heat. The word latent means hidden.
Liquid to solid:
-
The process of change from the liquid state to solid state at a particular temperature is called freezing.
-
Freezing point: It is the temperature at which liquid changes into solid at normal pressure.
-
On cooling, the potential energy is released in the form of heat energy. Intermolecular distance decreases and the force of attraction increases, the liquid thus starts changing into the solid state.
Liquid To Gas Change: (Vapourisation)
-
The process of change of liquid state to gaseous state is called vaporization.
-
When a liquid is heated, the molecules absorb the heat energy which gets accumulated as potential energy. On further heating intermolecular distance increases, intermolecular force becomes almost negligible, potential energy changes into kinetic energy and molecules escape as gas.
-
On cooling potential energy is released in the form of heat, intermolecular distance decreases up to a great extent, the force of attraction increases and the gaseous state changes to the liquid state.
-
Evaporation is a slow process. It occurs at all temperatures. Wet floor, after some time becomes dry because water from its surface evaporates.
-
The larger the surface area the faster the evaporation.
-
When evaporation occurs, the remaining liquid on the surface becomes cooler.
-
The temperature of water, kept in an open vessel is always lower than the temperature of water kept in a covered vessel.
Boiling:
-
Boiling is the process of change of liquid to vapour rapidly at a particular temperature and from all the parts of liquid.
-
When a liquid boils kinetic energy of the liquid molecule increases and the molecule acquires sufficient kinetic energy to overcome the force of attraction exerted on it by the other molecules.
-
When this happens, the molecules begin to leave the liquid at the surface and near the walls of the vessel.
-
The bubbles are formed at the surface and near the walls of vessel.
-
The bubbles grow in size with further evaporation and move to the surface in quick succession. This causes agitation in the entire mass of liquid. At this stage liquid is said to be boiling.
-
When boiling begins the entire heat supplied is used for setting the molecules free from each other. It enables them to escape as gas or vapour.
-
Boiling point is the constant temperature at which liquid changes to vapour under normal atmospheric pressure (1 atmospheric pressure).
-
Each liquid has characteristic boiling point of its own. The boiling point of alcohol is 78ºC, water is 100ºC.
-
Boiling point depends on pressure. It increases when the pressure is increased.
|
Evaporation
|
Boiling
|
|
It is a slow process.
|
It is a rapid process.
|
|
It takes place at the surface of the liquid.
|
It takes place throughout and is bulk phenomenon.
|
|
It takes place at all temperatures.
|
It takes place at the definite and constant temperature of the liquid(called the boiling point)
|
|
The temperature of the liquid falls.
|
The temperature of the liquid remains constant till the liquid changes to the vapour.
|
