WEATHER AND CLIMATE
-
Both weather and climate affect our lives in many ways.
-
Our way of living, the clothes we wear, the crops we grow, the food we eat, and many other things depend on the weather and climate of the place that we live in.
-
Many factors such as temperature, rainfall, humidity, etc., determine the weather of a place. Scientists monitor these 'weather factors' every day by using specially designed instruments like maximum-minimum thermometer, hygrometer, rain gauge, etc.
-
A special thermometer called the maximum-minimum thermometer is used to measure the maximum and minimum temperatures in a day.

Maximum- minimum thermometer
-
The relative humidity of the air is measured by an instrument called hygrometer.

Hygrometer
-
The amount of rainfall is measured by an instrument called the rain gauge.


Rain gauge
Factors That Affect the Climate of the Earth:
-
The climate of the Earth has not remained the same through the ages. There have been periods when it has been extremely cold, like in the Ice Age, when large areas of the Earth's surface were covered with ice.
-
With the advance in science and technology and powerful computers, scientists are now able to simulate the Earth's climate using a simplified model and study how various factors affect it.
-
The study of climate is fast emerging to be a very exciting and challenging field of science.
Climate of Earth as a Whole:
-
Some of the factors that affect the climate of planet Earth as a whole are:
-
The distance from the sun
-
The Earth's tilt
Distance from the Sun:
-
Earth, the planet we live on, is the third planet from the sun.
Data on the Earth and the Sun
|
(1)
|
Equatorial radius of the Earth
|
6378 km
|
|
(2)
|
Approximate radius of the Sun
|
6.96 × 108 m
|
|
(3)
|
Average distance between the Earth and the Sun
|
1.496 × 1011 m
|
|
(4)
|
Surface temperature of the Sun
|
6000 oC
|
|
(5)
|
Mass of the Earth
|
5.976 × 1024 kg
|
|
(6)
|
Mass of the Sun
|
1.989 × 1030 kg
|
-
The planet closest to the sun is much hotter than the planet farther away from it. This is because the sun is like a hot ball of fire.
-
Thus, the distance from the sun plays a major role in determining the temperature on the Earth's surface and, therefore, its climate.
Earth's Tilt:
-
The Earth rotates about its axis (which is an imaginary-line joining the North Pole and the South Pole).
-
The axis about which the Earth rotates is at a tilt with the plane of its orbit around the sun.
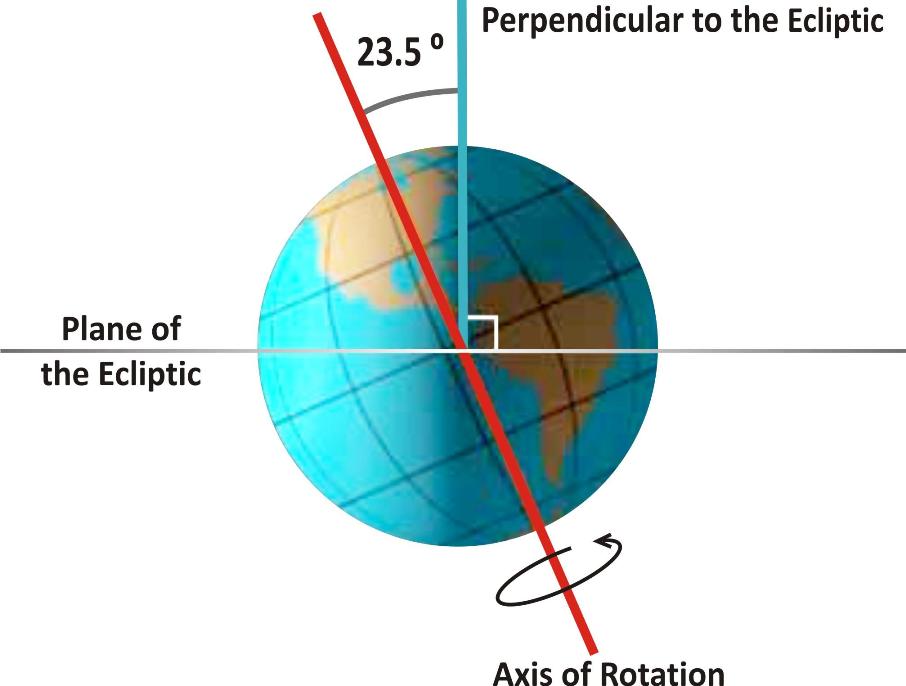
Earth's Tilt
-
The angle that the Earth's axis of rotation makes to the direction perpendicular to the plane of the Earth's orbit around the sun is called angle of inclination. This is about 23.5°.
-
Distance from the sun does not always determine the hotness and coldness of a planet.
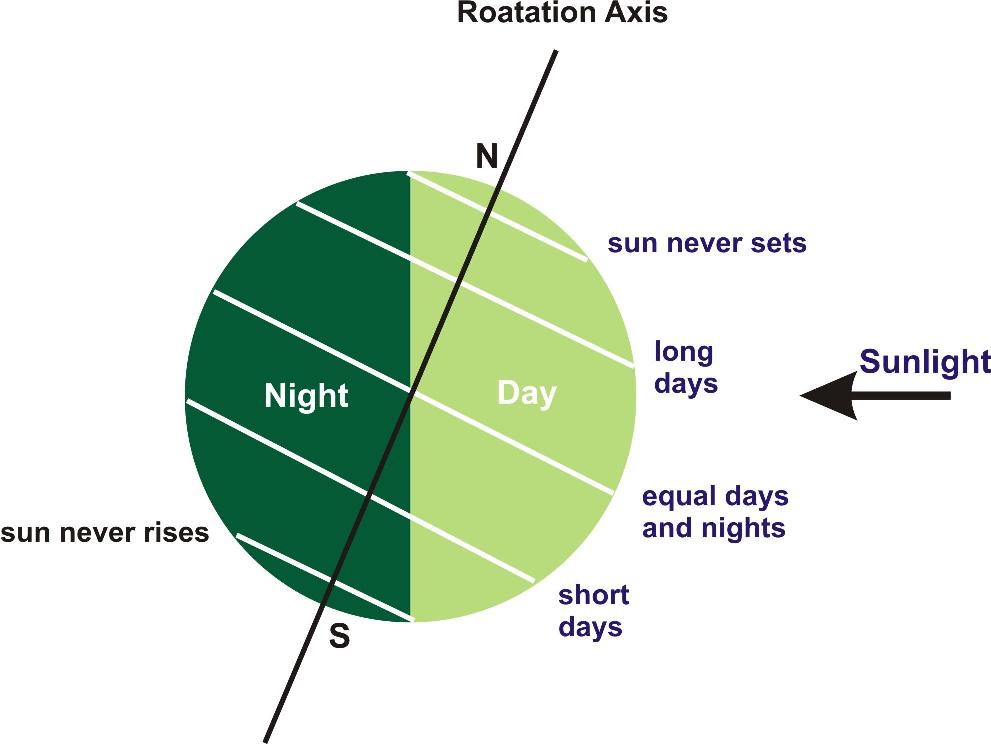
For example:
-
Even though Mercury is closer to the sun, it is a little colder than Venus. This is because Venus has a thick atmosphere of carbon dioxide.
-
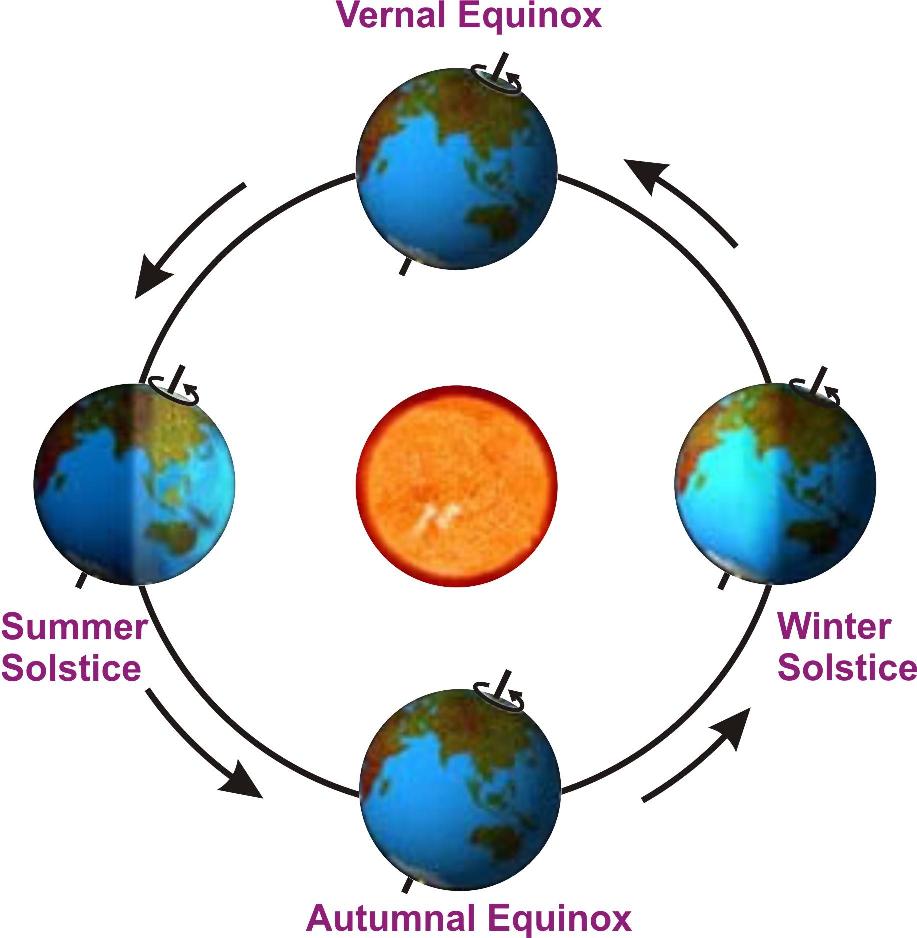
It is this tilt in the Earth's axis as well as revolution of the Earth around the sun that causes the occurrence of seasons on the Earth.
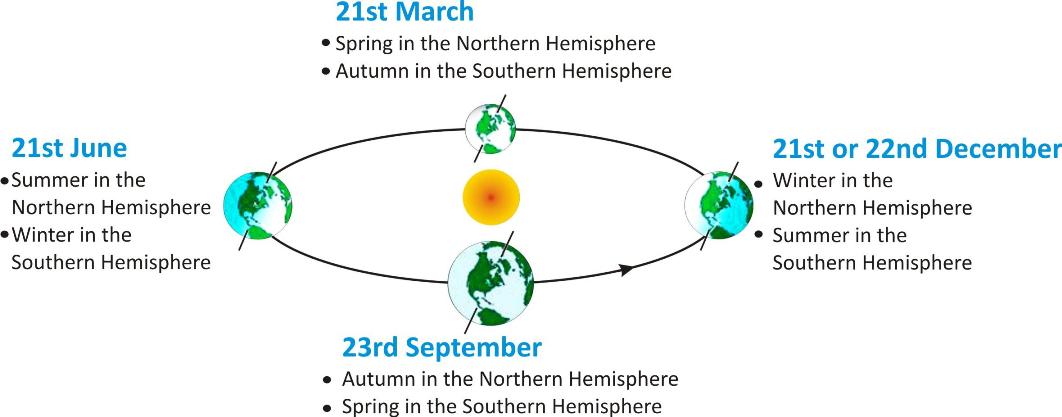
Changes of seasons on the Earth
-
From 21st March to 23rd September, the Northern hemisphere is closer to the sun.
-
So it is hotter than the Southern hemisphere, which is a little farther away from the sun.
-
The reverse happens in the next half of the orbit.
Sunrise and Sunset:
-
The length of a day is given by the difference in the times of the sunrise and sunset.
-
It is not the same throughout the year because the area of the Earth's surface lit by the sun varies due to the Earth's tilt and its position in its orbit around the sun.
-
In the Northern hemisphere, the longest day of the year is around 22nd June and the shortest day is around 22nd December.







