AIR POLLUTION
-
Air pollution is defined as the undesirable physical, chemical and biological changes in the air due to various natural processes or manual activities that disturb the environment and affect the biological health.
Causes of air pollution:
-
Components that cause the air pollution are known as pollutants. Air pollutants are eliminated in the environment due to natural processes or manual activities.
-
Examples: Carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, oxides of nitrogen and sulphur, suspended particles, dust, CFC’s etc.
Natural causes:
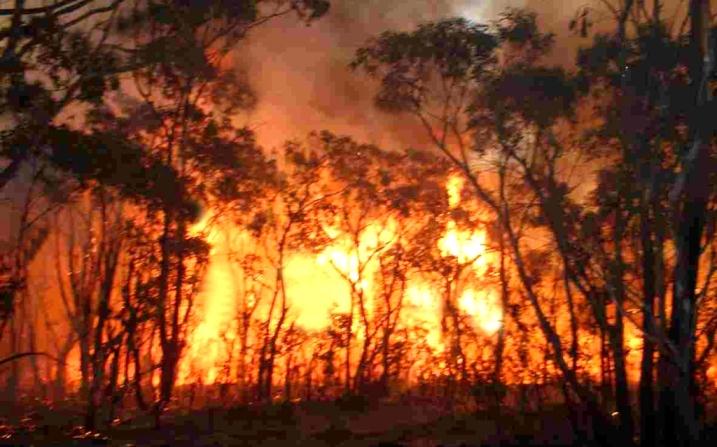
Forest fire:
-
A forest fire is a natural disaster which consists of burning of forest area that damages the wildlife and affects human health also.

-
Emissions from the forest fire can travel a long distance and can affect the quality of air and biological health.
Volcanoes:
-
Volcanic eruption is one of the most important natural causes of air pollution.

-
The most problematic gases emitted in a volcanic eruption include sulfur dioxide, carbon dioxide and hydrogen fluoride.
-
Besides the volcanic gases, volcanic ash is also formed. Volcanic ash can move hundreds to thousands of miles downwind from a volcano.
-
Fresh volcanic ash is gritty, rough and at times corrosive which can cause respiratory problems in human beings.
-
Volcanic eruptions can generate large amount of polluting gases and ash into the air due to which the sun’s rays could be blocked and land temperature in the affected area is lowered.
Dust storms:
-
A dust storm or sand storm is a meteorological phenomenon common in arid and semi-arid regions.

-
Dust storms arise when strong wind blows loose sand and dirt from a dry surface.
-
Particles are transported by a process that moves soil from one place and deposits it in another.
Man-made causes:
Deforestation:
-
Deforestation is defined as cutting of trees at a large scale and rapid rate.
-
As the population is increasing, deforestation is done for residential, agricultural and other basic requirements.

-
Deforestation causes the permanent destruction of forest that result in disturbance of biogeochemical cycles.
Combustion of fossil fuels:
-
The fossil fuels like coal and petroleum contain small amount of nitrogen and sulphur.
-
When these fuels are burnt, nitrogen and sulphur too are burnt thus producing their different oxides.
-
The combustion of fossil fuels also increases the amount of suspended particles in air. Suspended particles are the carbon particles produced due to incomplete combustion of fuel. These particles are also called as suspended particulate matter (SPM).
-
Accumulation of oxides of nitrogen, sulphur and carbon causes disturbance in the environment and damage to abiotic and biotic components.
-
They are used for different purposes and release different pollutants in the environment.
-
Automobiles: By the combustion of petrol or diesel, used in vehicles, carbon dioxide, and other poisonous gases like carbon monoxide, oxides of sulphur and nitrogen are produced which mixes with air.

-
Industries: Because of burning of coal in factories, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide are produced. These gases combine with moisture (water) in air and produce acid which is harmful.

-
Thermal power plants emit ashes, CO etc.

Industrial effluents (Gases):
-
Waste generated from the industries is known as effluent. Besides combustion of fossil fuels, the gaseous effluents produced due to chemical reactions are also eliminated from the chimneys. These contain toxic and dangerous components like minute particles of metallic oxides, hydrocarbons and gaseous residues that cause the air pollution.

Mining:
-
Air pollution from coal mines is mainly due to emissions of suspended particulate matter and gases including methane (CH4), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and oxides of nitrogen (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO) etc.
Overgrazing:
-
Overgrazing of grass or plants lead to the deforestation and thus affect the quality of air.

Solid waste:
-
Decomposition of accumulated waste in open areas release persistent toxic gases in the environment that damages the environment.

CFC’s:
-
Chloro fluro carbons or freons are extensively used as coolants in refrigerators and air conditioners and as propellants in home insulation, foam, metallic cans etc. they are not decomposed readily in environment and cause ozone layer depletion.










